Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
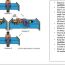
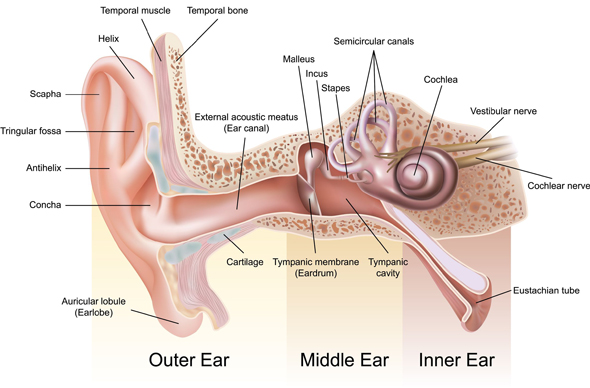
Eustachian Tube (ET) is a tube like structure which connects middle ear to the back of nose (nasopharynx). ET is partly cartilaginous (elastic bone) and partly bony. The cartilaginous part is near the back of the nose (nasopharynx) and bony part is near the middle ear.
ET helps to maintain pressure in the middle ear (middle ear ventilation) which is essential for the hearing mechanism. This is achieved automatically each time we yawn, swallow, sneeze etc.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is the failure of the Eustachian tube to adequately ventilate the middle ear.
What are the causes for ETD?
- Swelling at the back of nose due to sinusitis, large adenoids
- Narrowing of eustachian tube itself
What are the symptoms of ETD?
- Pressure in the ears
- Pain in the ear
- A feeling that your ears are clogged or under water
- Ear problems when you have a cold or sinusitis or in an aeroplane (Otitic barotrauma)
- Crackling or popping sounds in the ear
- Ringing in the ears
- A feeling that your hearing is muffled
The above can happen in one or both ears
What are the tests?
- Hearing test (Pure Tone Audiometry and Tympanometry)
- Nasal endoscopy to physically look at the eustachian opening at the back of nose (done in clinic)
- ETD Questionnaire
Medical treatment
- Treat nose and sinus infections
- Steroid nasal spray
- Otovent inflation device
Surgical intervention
- ET Balloon dilatation
Does it require general anaesthesia?
Yes
How long will it take?
Around 30 minutes and is performed as a day case
When can I return to work?
2 days time
What are the complications?
This is a fairly safe and minimally invasive procedure.
NICE (National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence). No complications were reported. One study showed more than 60% patients noted improvement in their symptoms. NICE recommends this as relatively safe and that it has the potential for significant impact, both for patients and the NHS, if shown to be efficacious.
Eustachian Tube dilatation is a fairly new procedure in the UK. It is a straight forward procedure. Some people don't get much benefit.
Regarding complications: injury to eustachian tube itself causing scarring, ear infection, pain and hearing loss.
Can this be coupled with any other procedures?
ETD is commonly noted in people with sinusitis. Hence the same balloon can be used to dilate the opening of sinuses (Balloon sinuplasty) at the same time.
What are the alternative treatment options?
- Medical treatment as mentioned above
- Insertion of grommets (ventilation tubes) in the ear. This carries risk of ear drum perforation, scarring of ear drum, early extrusion of grommets.
Can this be used in children?
At present this is not recommended in children.